Rice's theorem
In computability theory, Rice's theorem states that, for any non-trivial property of partial functions, there is no general and effective method to decide whether an algorithm computes a partial function with that property. Here, a property of partial functions is called trivial if it holds for all partial computable functions or for none, and an effective decision method is called general if it decides correctly for every algorithm. The theorem is named after Henry Gordon Rice, and is also known as the Rice-Myhill-Shapiro theorem after Rice, John Myhill, and Norman Shapiro.
Contents |
Introduction
Another way of stating Rice's theorem that is more useful in computability theory follows.
Let S be a set of languages that is nontrivial, meaning
- there exists a Turing machine that recognizes a language in S
- there exists a Turing machine that recognizes a language not in S
Then, it is undecidable to determine whether the language decided by an arbitrary Turing machine lies in S.
In practice, this means that there is no machine that can always decide whether the language of a given Turing machine has a particular nontrivial property. Special cases include the undecidability of whether a Turing machine accepts a particular string, whether a Turing machine recognizes a particular recognizable language, and whether the language recognized by a Turing machine could be recognized by a nontrivial simpler machine, such as a finite automaton.
It is important to note that Rice's theorem does not say anything about those properties of machines or programs which are not also properties of functions and languages. For example, whether a machine runs for more than 100 steps on some input is a decidable property, even though it is non-trivial. Implementing exactly the same language, two different machines might require a different number of steps to recognize the same input. Similarly, whether a machine has more than 5 states is a decidable property. Where a property is of the kind that either of the two machines may or may not have it, while still implementing exactly the same language, the property is of the machines and not of the language, and Rice's Theorem does not apply.
Using Rogers' characterization of acceptable programming systems, Rice's Theorem may essentially be generalized from Turing machines to most computer programming languages: there exists no automatic method that decides with generality non-trivial questions on the black-box behavior of computer programs.
As an example, consider the following variant of the halting problem: Take the property a partial function F has if F is defined for argument 1. It is obviously non-trivial, since there are partial functions that are defined for 1 and others that are undefined at 1. The 1-halting problem is the problem of deciding of any algorithm whether it defines a function with this property, i.e., whether the algorithm halts on input 1. By Rice's theorem, the 1-halting problem is undecidable.
Formal statement
Let 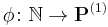 be a Gödel numbering of the computable functions; a map from the natural numbers to the class
be a Gödel numbering of the computable functions; a map from the natural numbers to the class 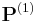 of unary (partial) computable functions. Denote by
of unary (partial) computable functions. Denote by 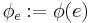 the
the 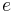 th (partial) computable function.
th (partial) computable function.
We identify each property that a computable function may have with the subset of 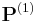 consisting of the functions with that property. Thus given a set
consisting of the functions with that property. Thus given a set 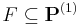 , a computable function
, a computable function 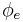 has property F if and only if
has property F if and only if 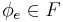 . For each property
. For each property 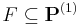 there is an associated decision problem
there is an associated decision problem 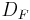 of determining, given e , whether
of determining, given e , whether 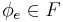 .
.
Rice's theorem states that the decision problem 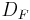 is decidable (also called recursive or computable) if and only if
is decidable (also called recursive or computable) if and only if 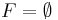 or
or 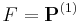 .
.
Examples
According to Rice's theorem, if there is at least one computable function in a particular class C of computable functions and another computable function not in C then the problem of deciding whether a particular program computes a function in C is undecidable. For example, Rice's theorem shows that each of the following sets of computable functions is undecidable:
- The class of computable functions that return 0 for every input, and its complement.
- The class of computable functions that return 0 for at least one input, and its complement.
- The class of computable functions that are constant, and its complement.
Proof by Kleene's recursion theorem
A corollary to Kleene's recursion theorem states that for every Gödel numbering 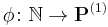 of the computable functions and every computable function
of the computable functions and every computable function 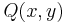 , there is an index
, there is an index 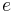 such that
such that 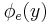 returns
returns 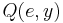 . (In the following, we will say that
. (In the following, we will say that 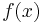 "returns"
"returns" 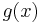 if either
if either  , or both
, or both 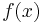 and
and 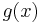 are undefined.) Intuitively,
are undefined.) Intuitively, 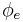 is a quine, a function that returns its own source code (Gödel number), except that rather than returning it directly,
is a quine, a function that returns its own source code (Gödel number), except that rather than returning it directly, 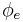 passes its Gödel number to
passes its Gödel number to 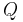 and returns the result.
and returns the result.
Let 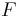 be a set of computable functions such that
be a set of computable functions such that 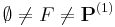 . Then there are computable functions
. Then there are computable functions 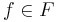 and
and 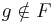 . Suppose that the set of indices
. Suppose that the set of indices  such that
such that 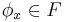 is decidable; then, there exists a function
is decidable; then, there exists a function 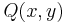 that returns
that returns 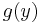 if
if 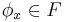 ,
, 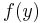 otherwise. By the corollary to the recursion theorem, there is an index
otherwise. By the corollary to the recursion theorem, there is an index 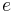 such that
such that 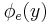 returns
returns 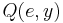 . But then, if
. But then, if 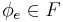 , then
, then 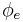 is the same function as
is the same function as 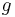 , and therefore
, and therefore 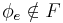 ; and if
; and if 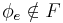 , then
, then 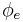 is
is  , and therefore
, and therefore 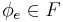 . In both cases, we have a contradiction.
. In both cases, we have a contradiction.
Proof by reduction from the halting problem
Proof sketch
Suppose, for concreteness, that we have an algorithm for examining a program p and determining infallibly whether p is an implementation of the squaring function, which takes an integer d and returns d2. The proof works just as well if we have an algorithm for deciding any other nontrivial property of programs, and will be given in general below.
The claim is that we can convert our algorithm for identifying squaring programs into one which identifies functions that halt. We will describe an algorithm which takes inputs a and i and determines whether program a halts when given input i.
The algorithm is simple: we construct a new program t which (1) temporarily ignores its input while it tries to execute program a on input i, and then, if that halts, (2) returns the square of its input. Clearly, t is a function for computing squares if and only if step (1) halts. Since we've assumed that we can infallibly identify program for computing squares, we can determine whether t is such a program, and therefore whether program a halts on input i. Note that we needn't actually execute t; we need only decide whether it is a squaring program, and, by hypothesis, we know how to do this.
t(n) {
a(i)
return n×n
}
This method doesn't depend specifically on being able to recognize functions that compute squares; as long as some program can do what we're trying to recognize, we can add a call to a to obtain our t. We could have had a method for recognizing programs for computing square roots, or programs for computing the monthly payroll, or programs that halt when given the input "Abraxas", or programs that commit array bounds errors; in each case, we would be able to solve the halting problem similarly.
Formal proof
For the formal proof, algorithms are presumed to define partial functions over strings and are themselves represented by strings. The partial function computed by the algorithm represented by a string a is denoted Fa. This proof proceeds by reductio ad absurdum: we assume that there is a non-trivial property that is decided by an algorithm, and then show that it follows that we can decide the halting problem, which is not possible, and therefore a contradiction.
Let us now assume that P(a) is an algorithm that decides some non-trivial property of Fa. Without loss of generality we may assume that P(no-halt) = "no", with no-halt being the representation of an algorithm that never halts. If this is not true, then this will hold for the negation of the property. Since P decides a non-trivial property, it follows that there is a string b that represents an algorithm and P(b) = "yes". We can then define an algorithm H(a, i) as follows:
- 1. construct a string t that represents an algorithm T(j) such that
- T first simulates the computation of Fa(i)
- then T simulates the computation of Fb(j) and returns its result.
- 2. return P(t).
We can now show that H decides the halting problem:
- Assume that the algorithm represented by a halts on input i. In this case Ft = Fb and, because P(b) = "yes" and the output of P(x) depends only on Fx, it follows that P(t) = "yes" and, therefore H(a, i) = "yes".
- Assume that the algorithm represented by a does not halt on input i. In this case Ft = Fno-halt, i.e., the partial function that is never defined. Since P(no-halt) = "no" and the output of P(x) depends only on Fx, it follows that P(t) = "no" and, therefore H(a, i) = "no".
Since the halting problem is known to be undecidable, this is a contradiction and the assumption that there is an algorithm P(a) that decides a non-trivial property for the function represented by a must be false.
Rice's theorem and index sets
Rice's theorem can be succinctly stated in terms of index sets:
-
Let
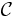 be a class of partial recursive functions with index set
be a class of partial recursive functions with index set 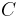 . Then
. Then 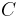 is recursive if and only if
is recursive if and only if 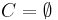 or
or 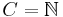 .
.
where 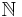 is the set of natural numbers, including zero.
is the set of natural numbers, including zero.
An analogue of Rice's theorem for recursive sets
One can regard Rice's theorem as asserting the impossibility of effectively deciding for any recursively enumerable set whether it has a certain nontrivial property.[1] In this section, we give an analogue of Rice's theorem for recursive sets, instead of recursively enumerable sets.[2] Roughly speaking, the analogue says that if one can effectively determine for any recursive set whether it has a certain property, then finitely many integers determine whether a recursive set has the property. This result is analogous to the original Rice's theorem because both assert that a property is "decidable" only if one can determine whether a set has that property by examining for at most finitely many 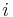 (for no
(for no 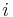 , for the original theorem), if
, for the original theorem), if 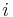 belongs to the set.
belongs to the set.
Let 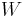 be a class (called a simple game and thought of as a property) of recursive sets. If
be a class (called a simple game and thought of as a property) of recursive sets. If 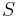 is a recursive set, then for some
is a recursive set, then for some 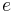 , computable function
, computable function 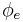 is the characteristic function of
is the characteristic function of 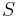 . We call
. We call 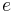 a characteristic index for
a characteristic index for 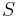 . (There are infinitely many such
. (There are infinitely many such 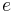 .) Let's say the class
.) Let's say the class 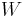 is computable if there is an algorithm (computable function) that decides for any nonnegative integer
is computable if there is an algorithm (computable function) that decides for any nonnegative integer 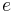 (not necessarily a characteristic index),
(not necessarily a characteristic index),
- if
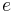 is a characteristic index for a recursive set belonging to
is a characteristic index for a recursive set belonging to 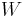 , then the algorithm gives "yes";
, then the algorithm gives "yes"; - if
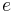 is a characteristic index for a recursive set not belonging to
is a characteristic index for a recursive set not belonging to 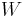 , then the algorithm gives "no".
, then the algorithm gives "no".
A set 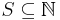 extends a string
extends a string  of 0's and 1's if for any
of 0's and 1's if for any 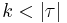 (the length of
(the length of  ), the
), the 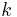 th element of
th element of  is 1 if
is 1 if 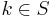 ; is 0 otherwise. For example,
; is 0 otherwise. For example, 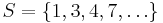 extends string
extends string 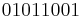 . A string
. A string  is winning determining if any recursive set extending
is winning determining if any recursive set extending  belongs to
belongs to 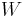 . A string
. A string  is losing determining if no recursive set extending
is losing determining if no recursive set extending  belongs to
belongs to 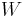 .
.
We can now state the following analogue of Rice's theorem (Kreisel, Lacombe, and Shoenfield, 1959,[3] Kumabe and Mihara, 2008[4]):
A class 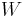 of recursive sets is computable if and only if there are a recursively enumerable set
of recursive sets is computable if and only if there are a recursively enumerable set 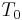 of losing determining strings and a recursively enumerable set
of losing determining strings and a recursively enumerable set 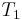 of winning determining strings such that any recursive set extends a string in
of winning determining strings such that any recursive set extends a string in 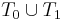 .
.
This result has been applied to foundational problems in computational social choice (more broadly, algorithmic game theory). For instance, Kumabe and Mihara (2008,[4] 2008[5]) apply this result to an investigation of the Nakamura numbers for simple games in cooperative game theory and social choice theory.
See also
Notes
- ^ A set
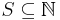 is recursively enumerable if
is recursively enumerable if 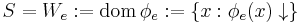 for some
for some 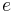 , where
, where 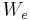 is the domain
is the domain 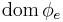 (the set of inputs
(the set of inputs  such that
such that 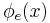 is defined) of
is defined) of 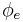 . The result for recursively enumerable sets can be obtained from that for (partial) computable functions by considering the class
. The result for recursively enumerable sets can be obtained from that for (partial) computable functions by considering the class 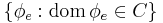 , where
, where 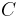 is a class of recursively enumerable sets.
is a class of recursively enumerable sets. - ^ A recursively enumerable set
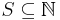 is recursive if its complement is recursively enumerable. Equivalently,
is recursive if its complement is recursively enumerable. Equivalently, 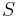 is recursive if its characteristic function is computable.
is recursive if its characteristic function is computable. - ^ Kreisel, G., Lacombe, D., Shoenfield, J.R., 1959. Partial recursive functionals and effective operations. In: Heyting, A. (Ed.), Constructivity in Mathematics. Studies in Logic and the Foundations of Mathematics. North-Holland, Amsterdam, pp. 290–297.
- ^ a b Kumabe, M.; Mihara, H. R. (2008). "Computability of simple games: A characterization and application to the core". Journal of Mathematical Economics 44: 348. doi:10.1016/j.jmateco.2007.05.012. http://econpapers.repec.org/paper/pramprapa/437.htm.
- ^ Kumabe, M.; Mihara, H. R. (2008). "The Nakamura numbers for computable simple games". Social Choice and Welfare 31: 621. doi:10.1007/s00355-008-0300-5. http://econpapers.repec.org/paper/pramprapa/3684.htm.
References
- Hopcroft, John; Ullman, Jeffrey (1979). Introduction to automata theory, languages, and computation. Addison-Wesley. pp. 185–192.
- Rice, H. G. "Classes of Recursively Enumerable Sets and Their Decision Problems." Trans. Amer. Math. Soc. 74, 358-366, 1953.
- Rogers, Hartley (1967). Theory of recursive functions and effective computability. New York: McGraw-Hill.
External links
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Rice's theorem" from MathWorld.